The REST API was a major feature of the 4.12 release and forms part of a broader ongoing change in the Cobalt Strike ecosystem. Therefore, we wanted to dedicate a blog post to explain the rationale behind it, discuss the architecture, and provide hands-on examples to get our customers up and running.
In addition to this blog, we will release a blog with more extensive examples that showcase the benefits of the REST API shortly, including an MCP server for integrating Cobalt Strike with the Claude LLM.
Our Motivation
Cobalt Strike was created over 15 years ago and whilst the product has changed a lot over this time, the architecture has remained the same: a fat client and a lightweight team server. This architecture has its benefits, such as the ability to collaborate via a team server whilst customizing and tinkering within the client to suit a specific way of working. However, we are always looking for opportunities to further open up Cobalt Strike to its users, provide new capabilities for offensive security research, and better support Red Team workflows. Therefore, we set out on an engineering journey to revamp the existing architecture and create a REST API.
Our main motivation for embarking on this journey was to bring the following capabilities to our customers:
- Language agnostic scripting in Cobalt Strike via REST: Users can customize the product with the tools and programming languages they’re most comfortable with.
- Server-side execution of Aggressor scripts: Users can run existing Aggressor/.cna scripts server-side and can call these scripts via the REST API.
- Better task tracking: Ability to relate tasks (i.e. commands) and their response, which is valuable for users working with the API and provides needed insights for LLMs.
- Server-side artifact storage: A multi-person red team can use one specific artifact (e.g. a BOF, Cobalt Strike payload or .NET assembly) across the full team.
- Roles or ‘command restrictions’: A junior operator or LLM can be restricted from running unauthorized functionality.
The Beta and Road Ahead
We decided to provide the Cobalt Strike REST API as a beta release. The community is an essential part of the Cobalt Strike ecosystem and this approach gives our users the chance to tinker with it and provide feedback on the overall design, as well as how it performs in real operations. In parallel, the Cobalt Strike team will continue development and add more features and functionality.
Although it is released as beta, we have a well thought-out set of API routes and the overall API has gone through the regular quality control and testing processes as other Cobalt Strike features. Therefore, we expect only minor changes to the currently exposed functionality, so anything built against this API should not require major changes in future releases.
Please note, the REST service is not yet feature complete, see section Scope and caveats of this beta at the bottom of this blog for more information.
What Has Changed
Cobalt Strike 4.12 introduced the following changes relating to the REST API:
- A new REST service that exposes Cobalt Strike functionality via a REST API.
- The team server now performs task-tracking and exposes the task/response relationship through the REST API and in the logs.
- A central location for artifact management (available via the REST API).
The REST API provides a language agnostic interface which can be used to rapidly develop custom automation flows, integrate Cobalt Strike into the realm of LLMs, and even create custom User interfaces/clients.
The following diagram provides an overview of the REST architecture. The team server and the csrestapi run on the same server, whilst the Cobalt Strike client continues to work in the same fashion.
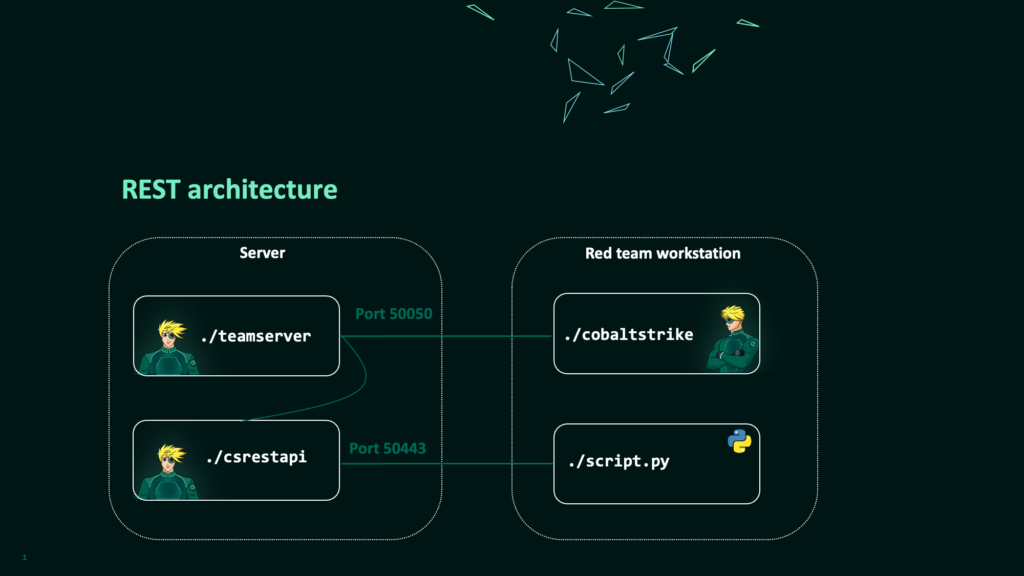
script.py over port 50443.Getting Started with REST
The following sections will explain how to start the REST service and provide some simple examples. In addition, we will explain some of the background in terms of API routes and their design. For simplicity, these examples use the Swagger UI and/or Curl. More information on OpenAPI and how to generate an SDK can be found in the section OpenAPI and Development SDK.
Starting the REST Service
The REST API is not started by default. To enable the database that facilitates persistent task tracking you must provide the new --experimental-db flag when starting the team server. Once the team server is up and running, the csrestapi can connect with the specified password and start exposing the REST API on port 50443.
./teamserver <ip > <password> [<profile> <kill_date>] -–experimental-db
./csrestapi –-pass $PASSWORD
To validate that the REST API runs successfully, a Swagger user interface should be accessible on https://<teamserver>:50443/.
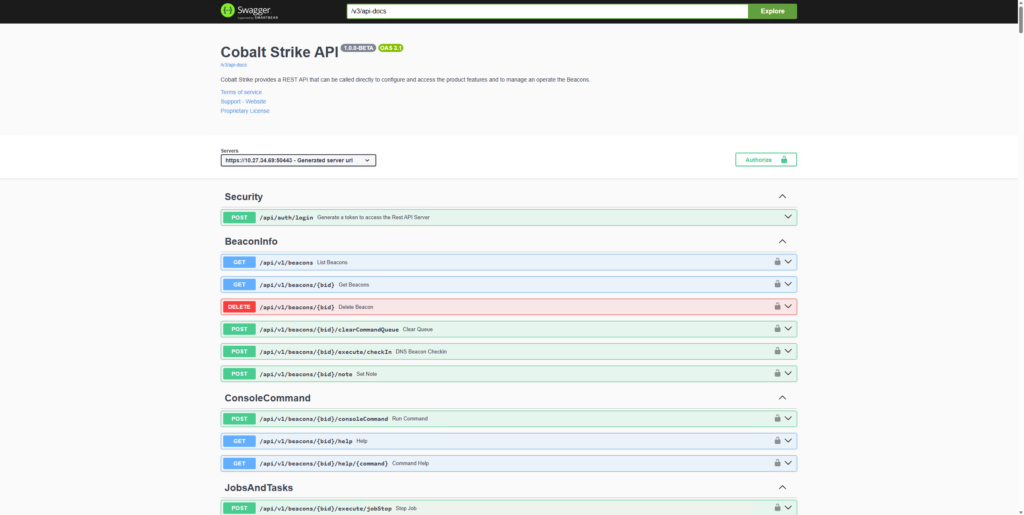
It is possible to configure different aspects of the REST API (e.g. network port, https certificates, etc) with startup flags and in the ./rest-server/application.properties file. More information can be found in the user guide.
Do not expose the REST API to the Internet. We recommend using network security controls (e.g. vpn), so that the interface is only exposed to authorized users.
Authentication and a First REST Request
To interact with the API, we first need to authenticate and obtain an access token via the /api/auth/login route. This takes a username and the team server password and returns an access token which must be included in each request in the Authorization HTTP header.
In the Swagger UI you can click the ‘authorize’ button and add the access token, so you don’t need to copy/paste this in every request.
Once we have obtained an access token, it is possible to use any of the requests shown in the Swagger UI. For example, we can use /api/v1/beacons to get a listing of currently active Beacons and their associated Beacon IDs. This request is particularly important, as we will need a Beacon ID to interact with a specific Beacon in the rest of the examples in this blog post.
The recording below demonstrates the process of starting the REST service, authenticating and listing running Beacons.
Video 1: Start up the REST service, authenticate and list Beacons via Swagger.
Console Command and Structured Commands
In the REST API we offer two ways of command execution:
- A consoleCommand route: This executes any input as if it was entered in the Cobalt Strike console.
- A structured command route: Each command/functionality is a separate REST endpoint, similar to individual aggressor functions. The benefit of the structured command routes is that the input and output is much more clearly defined (i.e. named parameters). Secondly, the structured commands will likely serve as a building block for roles and permissions in a future release. Therefore, we recommend using these structured commands over the consoleCommand route.
- /spawn/ – indicates that the command uses fork & run.
- /inject/ – indicates that the command injects into a specified process.
- /execute/ – indicates that the command relies on Windows API calls.
- /state/ – indicates a command that modifies Beacon’s configuration.
- Place the TrustedSec situational awareness collection on disk (e.g. in
restapi/scripts_folder/orrestapi/BOF/). - Add the filepath of
SA.cnainto thecna_scripts.configfile so the REST server will load it upon startup. - (re)start the csrestapi.
- The current REST API is not fully feature complete: The API supports the vast majority of Cobalt strike functionality. There are, however, some areas where the API is not (yet) complete:
- The reporting functionality and specific data models, such as services, sites and targets are not included.
- The resource kit/artifact kit and process inject kit are not yet exposed via REST. Thus exporting filetypes such as exe, dll, hta is currently not possible.
- Controlling the SSH Beacon is not supported via REST.
- There is a limited set of commands not ported over (e.g. GUI commands such as ‘history’). Please refer to the command to REST mapping for additional details.
- No roles, authorizations and command restrictions yet: The functionality for roles or ‘command restrictions’ as described in our motivations is not yet provided. However, we did design our API to facilitate this in future releases.
- Task tracking has imperfections: We added a fair share of task-management and state tracking in the team server. However, we also hit limits in the exact communication flows between Beacon and the team server. Further mitigating these imperfections required a larger overhaul of Beacon and its messaging. For now, it is known behavior that various tasks never get to the state
COMPLETEDbut remain in the stateOUTPUT_RECEIVEDorIN-PROGRESSif there is no output. For example, altering the sleep of a beacon will remainIN-PROGRESSindefinitely. - Not all features are backported in the native client: With the REST server, we introduce the concept of ‘server-side storage’. A user can store and use artifacts (e.g. a generated payload, a BOF, .cna or .net assembly) in the REST-storage so all operators can use the same version of a specific artifact via REST. However, this functionality is not yet natively implemented in the regular Cobalt Strike client. We do have a prototype Aggressor script which enables the execution of server-side artifacts from the Cobalt Strike GUI. We will polish this up and release it soon.
- Real-world experience and feedback is needed: The changes around tasking and central database storage within the team server needs real-world usage. We have done performance tests, but nothing beats the experience of our users.
- Release our internal prototypes, including our MCP server: As part of our internal research, testing, and QA process, we have created various internal prototypes that rely on REST. For example, we have made a Model Context Protocol (MCP) that integrates the Cobalt Strike REST API in an LLM, a ‘mobile webapp’ and Aggressor scripts to call into the REST API from the regular client. We believe these examples serve as excellent showcases to prove the power of this API. In the upcoming weeks, we will polish up the internal prototypes and release them.
- Further mature the REST API: As indicated earlier, in future releases we will further mature this API and we foresee it becoming a core component of the Cobalt Strike architecture.
- We want your feedback: Besides this release, we have also improved our feedback process. We have added a simple feedback form on our support page under the “Support” header which can be used to submit bugs, ask questions, or provide feedback on the REST Beta as well as on other features of the product.. You can also access this form directly from your Cobalt Strike client via
Help->Support.
The following two examples use a directory listing to demonstrate these requests:
consoleCommand
The consoleCommand route takes a command as if we typed it into the Cobalt Strike command line:
curl-k -X 'POST' \
'https://teamserver:50443/api/v1/beacons/$beaconID/consoleCommand' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"command": "ls c:\\users"
}'
execute/ls
The /execute/ls/ endpoint takes only the path argument as illustrated below:
curl-k -X 'POST' \
'https://teamserver:50443/api/v1/beacons/<$beaconID>/execute/ls' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"path": "c:\\users"
}'
Using Tasks to Retrieve Results
As the execution of a command relies on the exact moment when the Beacon checks-in, the REST requests cannot provide an immediate response. Consequently, the API creates a task and returns a taskID. This taskID can be used to retrieve the output or status as demonstrated below.
curl-k -X 'GET' \
'https://teamserver:50443/api/v1/tasks/$taskID?format=structured' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>
This recording illustrates the steps required for running an ls on a beacon and getting its output.
Video 2: : Run ‘ls’ via the structured route and collect its response via the task mechanism.
It is important to highlight that whilst introducing the structured command routes we deviated from the historical Cobalt Strike command naming and created a more consistent naming convention that more clearly expresses Beacon’s actions:
As an example, the execute-assembly command can be accessed as /spawn/dotnetAssembly, setting a new sleep value is done via /state/sleepTime and running ls is done via /execute/ls.
To help our users in finding the right routes, a mapping of all existing Cobalt Strike commands to their REST route is provided in our documentation. Furthermore, in the Swagger UI routes are grouped by functionality, making it easier to find related commands.
Artifacts and Server-side Storage
Various Cobalt Strike commands take a binary file as input (i.e. an artifact). For example, running a .NET assembly like Rubeus. The API uses the @files operator within various REST calls to indicate that the file itself is provided within the request as a base64 encoded file. In the example below, we request the API to run Rubeus via execute-assembly (REST route spawn/dotnetAssembly).
curl-k -X 'POST' \
'https://teamserver:50433/api/v1/beacons/<$beaconID>/spawn/dotnetAssembly' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"assembly": "@files/Rubeus.exe",
"arguments": "logonsession",
"files": {
"Rubeus.exe":"<base64=== >"
}
}'
Server-side Artifacts & Disk Structure
Server-side artifact storage makes it possible for one user to place artifacts (e.g. .NET assemblies, BOFs or .cna files) on the server and via REST those artifacts can be accessed and used by all users.
The table below lists the default folders and files created by the REST API that are intended for server-side artifact storage. Users are free to structure files according to their preference, with two exceptions. First, the generated folder is intended for any payloads generated by Cobalt Strike. Second, the cna_scripts.config file is used to configure which .cna scripts are loaded by default by the REST API.
Server-side Aggressor scripts that are run by REST are restricted to Sleep/Aggressor and cannot use any Java bindings.
| Path | Description |
| /rest-server/csrestapi | Mandatory/reserved files: the REST service binary itself and further dependencies in the rest-server folder |
| /rest-server/restapi/cna_scripts.config | Mandatory/reserved file: A text file with the paths to individual .cna files that are loaded globally by the REST service |
| /rest-server/restapi/artifacts/generated | Mandatory/reserved folder: reserved for payloads generated by the Cobalt Strike REST service |
| /rest-server/restapi/artifacts/assemblies | A folder intended for .NET assemblies |
| /rest-server/restapi/artifacts/sleepmasks | Folder intended for scripts and resources for Sleepmasks |
| /rest-server/restapi/artifacts/udrls | Folder intended for scripts and resources for UDRLs |
Since the REST API does not currently allow for file uploads, it is expected that users will place artifacts via SSH or other file copy means.
Running a .NET Assembly as a Server-side Artifact
The API’s server-side storage makes it possible for users to reference an artifact that is already present on the server, instead of sending it in the request.
The /api/v1/artifacts route allows users to list the available server-side artifacts and retrieve their symbolic references. These can then be used as part of any request that expects a binary file. In the example below, Rubeus.exe was previously uploaded to the restapi/artifacts/assemblies/ folder.
curl-k -X 'GET' \
'https://teamserver:50433/api/v1/artifacts' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
This will return the following:
[
{
"key": "assemblies/Rubeus.exe",
"symbolicReference": "@artifacts/assemblies/Rubeus.exe"
}
]
To execute the server-side Rubeus.exe, we can utilise the /spawn/dotnetAssembly route and provide the symbolic reference:
curl-k -X 'POST' \
'https://teamserver:50433/api/v1/beacons/<$beaconID>/spawn/dotnetAssembly' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"assembly": "@artifacts/assemblies/Rubeus.exe",
"arguments": "logonsession"}
'
This video demonstrates running Rubeus from server-side storage and collecting its output.
Video 3: Running a server-side.net assembly (Rubeus.exe) via REST.
Server-side Aggressor Scripts and Aliases
In addition to PE files and .NET assemblies, the server-side storage also supports Aggressor/.cna scripts. Upon startup of the REST API, any .cna filepath that is included in the cna_scripts.config file will automatically be loaded. To illustrate the value of this, we will deploy the TrustedSec Situational Awareness BOF collection server-side. The result is that all the aliases that are included in Situational Awareness become available via REST.
This involves the following deployment steps:
echo "restapi/scripts_folder/SA/CS-Situational-Awareness-BOF-master/SA/SA.cna" >> restapi/cna_scripts.config
Once the csrestapi is restarted, we can use the /help endpoint to verify that the Situational Awareness aliases are available.(e.g. the command probe or whoami from Situational Awareness should be listed in the output of /help.)
curl-k -X 'GET' \
'https://teamserver:50443/api/v1/beacons/<$beaconID>/help' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>'
Server-side aliases that are loaded by the REST API can be run via the consoleCommand, as shown below:
curl-k -X 'POST' \
'https:// teamserver:50443/api/v1/beacons/<$beaconID>/consoleCommand' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"command": "probe 127.0.0.1 445"
}'
The video below demonstrates the process steps as outlined above.
Video 4: Deploying the TrustedSec Situational Awareness collection and running the ‘whoami’ alias.
Server-side Payload Generation
It is also possible to generate payloads via REST; the resulting payloads can be retrieved or used via @artifacts within other calls towards the API.
In the following request a payload is being generated by the REST service and stored in the server-side storage.
curl –k -X 'POST' \
'https://teamserver:50433/api/v1/payloads/generate/stageless' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <$access_token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"listenerName": "https",
"useListenerGuardRails": true,
"guardRails": {
},
"architecture": "x64",
"exitFunction": "Process",
"systemCallMethod": "None",
"httpLibrary": "wininet",
"dnsCommMode": "dns",
"output": "Raw"
}'
This route has optional parameters for sleepMaskCNA and a udrlCNA that can point to an @artifacts reference so that payload generation can be fully customized. In the video below this functionality is demonstrated with the AceLDR UDLR.
Video 5: Server-side payload generation using custom .cna files and retrieval of the resulting payload.
OpenAPI & Development SDK
The examples provided thus far in this blog relied on Swagger and Curl. These serve as excellent examples to illustrate the API but are not the best suited to integrate in a mature programming language. As the Cobalt Strike REST API supports OpenAPI, it is possible to generate an SDK for a large variety of programming languages. On our GitHub we provide a Jupyter notebook with instructions on how to generate an SDK and use the API from Python.
This video demonstrates installing and using the OpenAPI SDK for Python.
Video 6: Using OpenAPI to generate a Python SDK.
Scope and Caveats of This Beta
The following should be considered when using the beta release of the REST API: